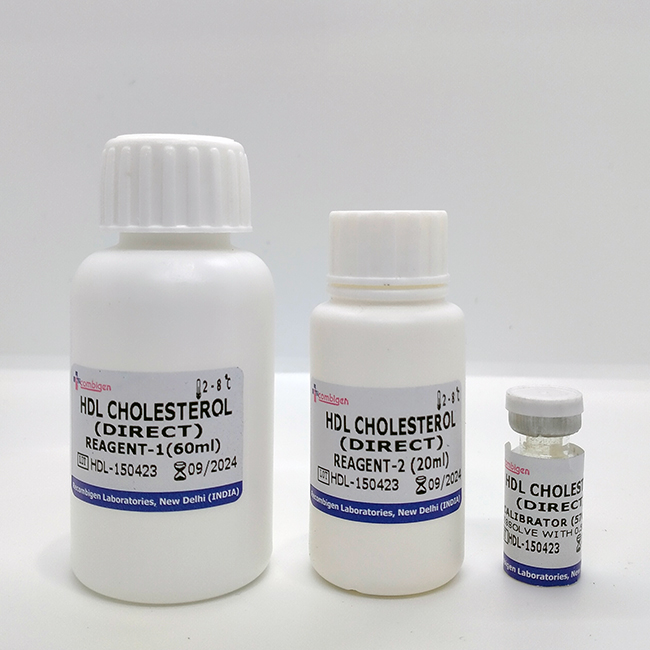
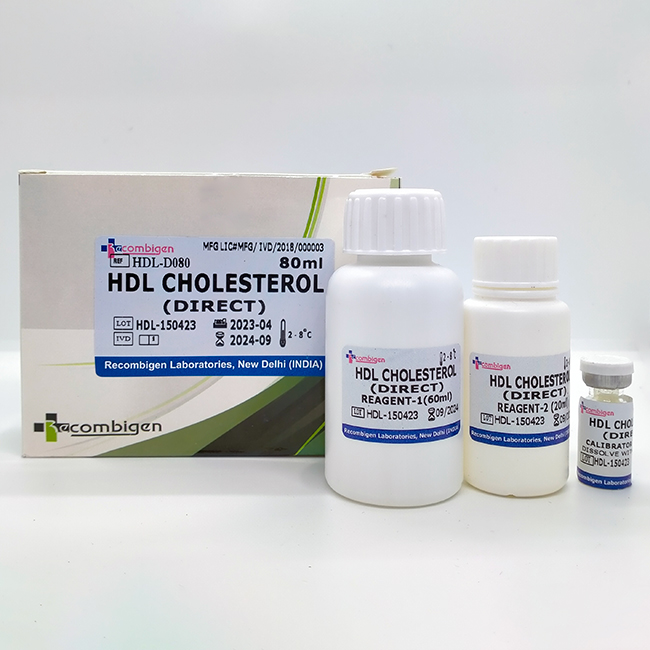
HDL-CHOLESTEROL (DIRECT)
₹5,280.00 ₹1,955.00
| Material |
Biochemistry Reagent
|
| Usage/Application |
Laboratory / Hospital / Pathology
|
| Tests Kit | KIT |
| Packaging Size | 80ML |
HDL-cholesterol, often referred to as high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, is a type of cholesterol that carried in the bloodstream by high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles. HDL considered “good” cholesterol because it plays a beneficial role in cardiovascular health.
The lipid profile typically includes measurements of total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol), and triglycerides.
HDL-cholesterol has several important functions:
1.) Reverse cholesterol transport: HDL particles transport cholesterol from the peripheral tissues, including arterial walls, back to the liver. This process helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of cholesterol buildup in the arteries.
2.) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties: HDL particles have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which help protect against the development of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by plaque formation in the arteries.
3.) Endothelial function improvement: HDL particles promote endothelial function, which refers to the health and proper functioning of the inner lining of blood vessels. Maintaining a healthy endothelium is crucial for preventing the development of cardiovascular diseases..
In general, higher levels of HDL-cholesterol are considered desirable because they are associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases. However, it’s important to interpret HDL-cholesterol levels in the context of the overall lipid profile, including LDL-cholesterol and triglyceride levels, as well as other risk factors for heart disease such as blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes.
| Weight | 0.300 g |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 17 × 14 × 6 cm |
1 review for HDL-CHOLESTEROL (DIRECT)
You must be logged in to post a review.

 Rapid Diagnostic Products
Rapid Diagnostic Products Serology Products
Serology Products Clinical Lab Accessories
Clinical Lab Accessories OTC Products
OTC Products Water Quality Test Kit
Water Quality Test Kit 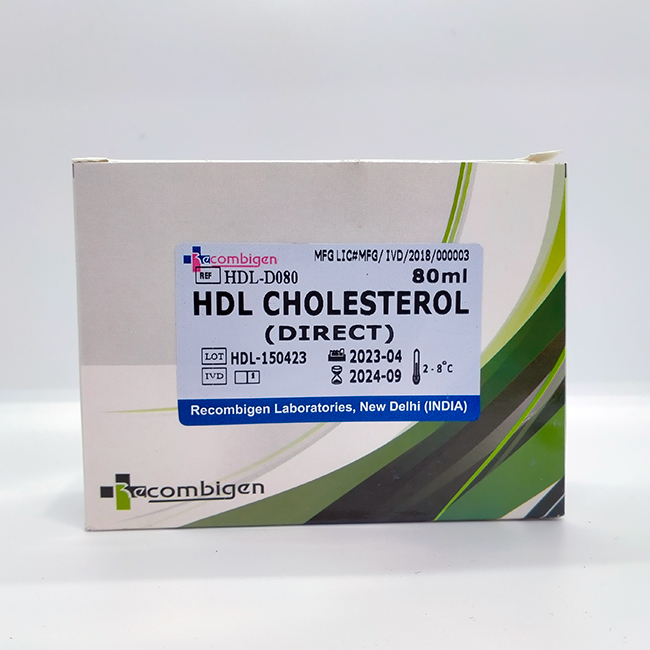







Darpan Laboratory –
price is too high.