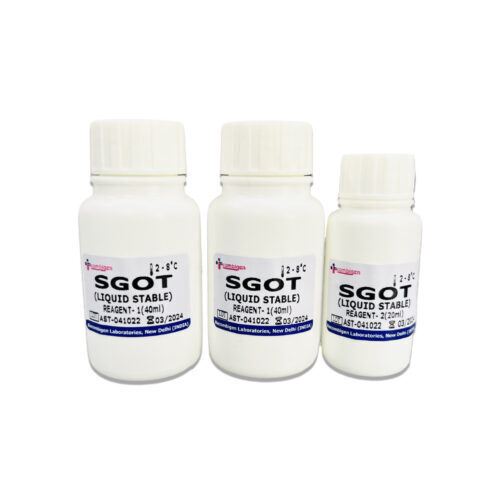
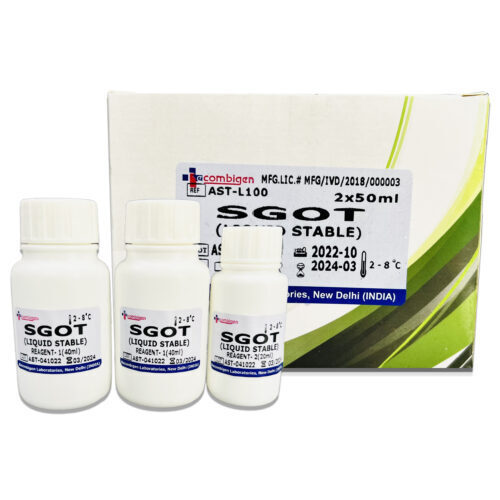
AST ( SGOT Reagents )
₹1,267.00 – ₹2,464.00
| Usage/Aplication |
Laboratory Chemical
|
| Brand |
Recombigen
|
| Packaging Type |
Box
|
| Shelf Life |
16 Month
|
| Country of Origin |
Made in India
|
SGOT (Serum Glutamic Oxaloacetic Transaminase), also known as AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase), is an enzyme found in various tissues throughout the body, with particularly high levels in the liver and heart. It is commonly measured in blood tests to evaluate liver and heart health.
Reagents are substances or compounds used in laboratory tests to facilitate a specific reaction or measurement. In the case of measuring SGOT levels, the most common reagents used are:
- Aspartate substrate: A substrate containing aspartate, which is acted upon by SGOT/AST to produce oxaloacetate and glutamate. This substrate is usually provided in a buffered solution.
- Coenzyme: Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) or pyridoxal-5-phosphate (P5P) is commonly used as a coenzyme for SGOT/AST. It acts as a cofactor in the transamination reaction, transferring the amino group between aspartate and α-ketoglutarate.
- Buffer solution: A solution with a defined pH that helps maintain the optimal conditions for the SGOT/AST reaction. The buffer solution ensures that the enzymatic reaction occurs at the appropriate pH range for accurate measurements.
- Reagent blanks: These are solutions that contain all the components of the assay except the sample being tested. Reagent blanks are used as control solutions to establish a baseline measurement for comparison.
- Calibration standards: A set of solutions with known concentrations of SGOT/AST are used to create a calibration curve. The calibration curve is used to determine the concentration of SGOT/AST in the sample being tested by comparing its reaction to the known standards.
It’s important to note that specific reagents may vary depending on the manufacturer or the assay method used in a particular laboratory. Different commercial kits or laboratory protocols may have slight variations in the composition of the reagents used for SGOT/AST measurement.
| Weight | 0.175 g |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 13 × 12 × 4 cm |
| ML | 2*50ML, 4*20ML, 5*50ML, 20*50ML |
You must be logged in to post a review.

 Rapid Diagnostic Products
Rapid Diagnostic Products Serology Products
Serology Products Clinical Lab Accessories
Clinical Lab Accessories OTC Products
OTC Products Water Quality Test Kit
Water Quality Test Kit 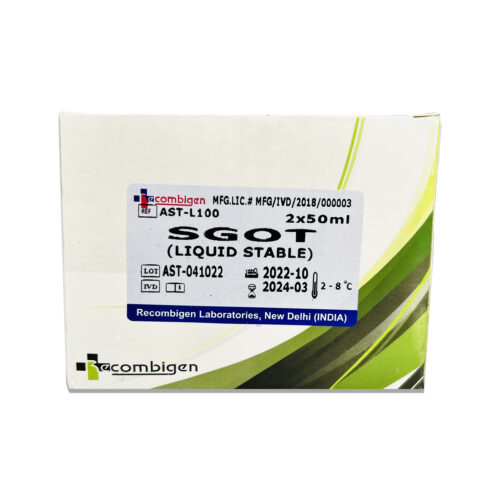









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.