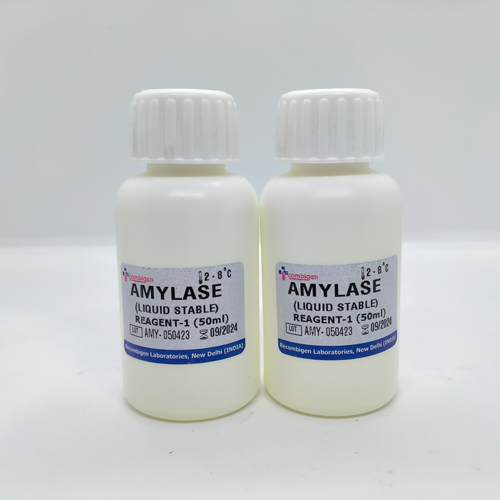
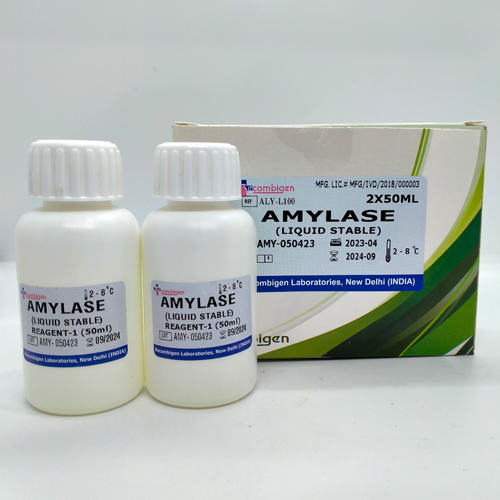
Amylase Reagent, For Laboratory
₹8,800.00 ₹2,100.00
| Usage/Application |
Laboratory
|
| Brand |
Amylase
|
| Shelf Life |
17 Month
|
| Packaging Size |
2*50 ml
|
| Country of Origin |
Made in India
|
Amylase reagent, also known as amylase assay reagent, is a chemical solution or mixture used to measure the activity or concentration of amylase enzyme in biological samples. Amylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of starch into smaller carbohydrate molecules such as maltose and glucose. Measurement of amylase activity or concentration is commonly performed in clinical laboratories to assess pancreatic and salivary gland function or diagnose conditions such as pancreatitis.
The composition of amylase reagent can vary depending on the specific assay or manufacturer. However, typical components of amylase reagent may include:
- Substrate: A specific substrate that is acted upon by amylase, such as starch or a starch derivative.
- Enzyme inhibitors: Some amylase reagents may contain inhibitors to prevent interference from other enzymes that could affect the measurement.
- Buffer: A buffer solution is included to maintain the optimal pH for the amylase reaction.
- Stabilizers and preservatives: Reagents may contain stabilizers and preservatives to enhance the stability and shelf life of the solution.
The specific instructions for using amylase reagent can vary based on the assay kit or manufacturer. In general, the procedure involves mixing the amylase reagent with the sample containing amylase, allowing the enzymatic reaction to occur, and measuring the resulting signal, such as color change or absorbance, using a spectrophotometer or other appropriate instrument. The amylase activity or concentration in the sample can then be determined by comparing the measured signal to a calibration curve generated from standards of known amylase activity or concentration.
It is important to follow the instructions provided with the specific amylase assay kit and ensure that the reagent is used within its specified shelf life and storage conditions. The manufacturer’s instructions will provide detailed information on the usage, handling, and interpretation of results for the amylase reagent.
| Weight | 0.0153 g |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 12 × 4 × 9 cm |
You must be logged in to post a review.

 Rapid Diagnostic Products
Rapid Diagnostic Products Serology Products
Serology Products Clinical Lab Accessories
Clinical Lab Accessories OTC Products
OTC Products Water Quality Test Kit
Water Quality Test Kit 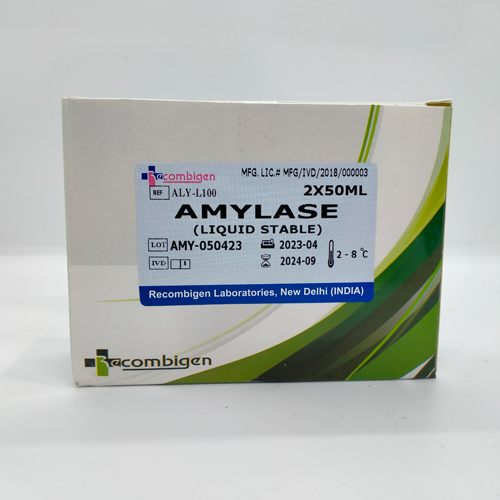








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.