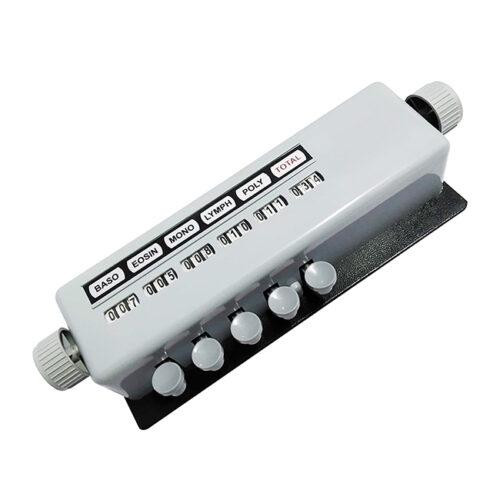
Blood Cell Counter 5 Key
₹1,350.00 ₹980.00
| Automation | Manual |
| Brand | Recombigen |
| Sample Mode | Whole Blood |
| Categories | Medical/Hospital |
| Differential Type | 5-Part |
What Is and How To Work Blood Cell Counter
The exact working principle of a blood cell counter can vary depending on the specific technology employed by the instrument. Here is a general overview of how a typical hematology analyzer works:
- Sample Preparation- A small volume of blood sample (usually obtained from a venous blood draw) and collected anticoagulated to prevent clotting. The sample is then loaded onto the blood cell counter for analysis.
- Cell Counting: The blood sample passes through a small aperture or flow cell within the analyzer. Various technologies can be used to count the cells. The most common methods include:
a. Impedance: This method relies on the principle that cells change the electrical resistance as they pass through an aperture. By measuring changes in electrical impedance, the analyzer can count and size the cells.
b. Flow Cytometry: Flow cytometry utilizes a laser or other light sources to illuminate the cells as they pass through a flow cell. The cells label with fluorescent dyes or antibodies that bind to different cellular components, allowing the analyzer to characterize and count the cells based on their fluorescence properties.
c. Optical Methods: Some analyzers use optical techniques, such as light scattering or absorption, to measure the properties of the cells. These methods can provide information about cell size, shape, and hemoglobin content.
- Analysis and Data Interpretation: The blood cell counter analyzes the raw data obtained from the cell counting process. It applies algorithms and mathematical models to interpret the data and determine the concentrations and characteristics of different types of cells, such as RBCs, WBCs, and platelets.
- Result Reporting: Once the analysis is complete, the hematology analyzer generates a comprehensive report with various parameters, including cell counts, cell sizes, hemoglobin levels, and other relevant information. These results are displayed on a screen or printed out for review and interpretation by healthcare professionals.
It’s important to note that different blood cell counters may have additional features and capabilities, such as differential WBC counts, reticulocyte analysis, or flagging abnormal cell populations for further investigation. The specific technology and features of a blood cell counter can vary depending on the manufacturer and model.
You must be logged in to post a review.

 Rapid Diagnostic Products
Rapid Diagnostic Products Serology Products
Serology Products Clinical Lab Accessories
Clinical Lab Accessories OTC Products
OTC Products Water Quality Test Kit
Water Quality Test Kit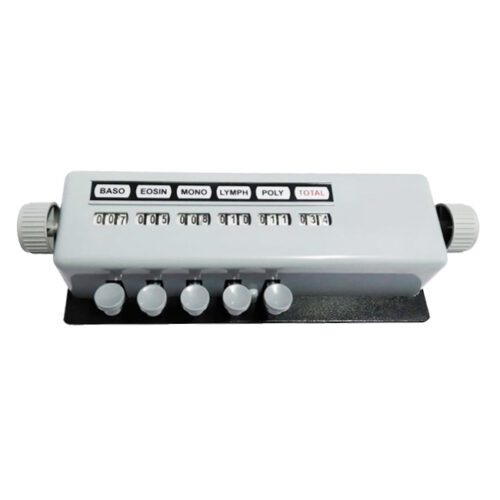 










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.